If your Windows PC fails to boot due to a corrupted bootloader, you can often resolve the issue using the Command Prompt from the Windows Recovery Environment (WinRE). This guide provides a step-by-step approach to repairing the Windows bootloader, applicable to both MBR (Master Boot Record) and GPT (GUID Partition Table) partition styles.
Prerequisites
Before proceeding, ensure you have:
- A bootable Windows installation media (USB or DVD).
- Knowledge of your system’s partition style (MBR or GPT).
Step-by-Step Guide to Repair the Windows Bootloader
- Access the Windows Recovery Environment (WinRE)
- Insert the Windows installation media into your PC.
- Restart your computer and boot from the installation media.
- On the Windows Setup screen, select your language preferences and click Next.
- Click on Repair your computer at the bottom-left corner.
- Navigate to Troubleshoot > Advanced options > Command Prompt.
- Identify the System Partition
In the Command Prompt:
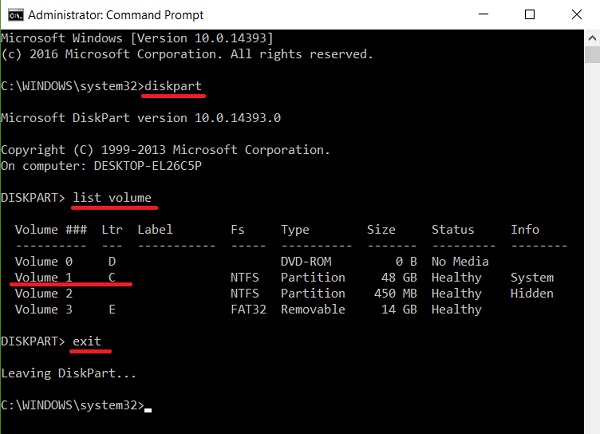
- Type diskpart and press Enter.
- Type list volume and press Enter.
- Identify the volume labeled as the EFI System Partition (for GPT) or the System Reserved partition (for MBR). Note the corresponding drive letter.
- Type exit and press Enter to leave DiskPart.
- Repair the Bootloader
For MBR Partition Style
- In the Command Prompt, type:
bash
CopyEdit
bootrec /fixmbr
and press Enter.
- Then type:
bash
CopyEdit
bootrec /fixboot
and press Enter.
- To rebuild the Boot Configuration Data (BCD), type:
bash
CopyEdit
bootrec /rebuildbcd
and press Enter.
For GPT Partition Style
- Assign a drive letter to the EFI partition if it doesn’t have one:
pgsql
CopyEdit
diskpart
list volume
select volume X (Replace X with the volume number of the EFI partition)
assign letter=Z (You can choose any available letter)
exit
- Navigate to the EFI boot directory:
bash
CopyEdit
cd /d Z:\EFI\Microsoft\Boot\
- Repair the boot sector:
bash
CopyEdit
bootrec /fixboot
- Rebuild the BCD:
bash
CopyEdit
bcdboot C:\Windows /s Z: /f ALL
Replace C:\Windows with the correct path if your Windows is installed on a different drive.
- Exit and Restart
- Type exit and press Enter to close the Command Prompt.
- Click on Continue to boot into Windows.
Additional Tips
- If you encounter an “Access is denied” error during bootrec /fixboot, ensure that the EFI partition is properly assigned a drive letter and formatted with the FAT32 file system.
- Use the bcdedit command to view and manage the boot configuration data.
- Always back up important data before performing system repairs.
Conclusion
Repairing the Windows bootloader using the Command Prompt is a straightforward process when following the correct steps. Whether your system uses MBR or GPT, the above guide provides the necessary commands to restore your PC’s boot functionality. Always ensure you have a backup of your data and the appropriate installation media before proceeding with system repairs.